Anti Money Laundering Analyst Job Description
What is Anti-Money Laundering?
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) is a set of policies, procedures, and technologies that prevents money laundering. It is implemented within government systems and large financial institutions to monitor potentially fraudulent activity.

Summary
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) is a set of policies, procedures, and technologies that prevents money laundering.
- There are three major steps in money laundering (placement, layering, and integration), and various controls are put in place to monitor suspicious activity that could be involved in money laundering.
- Some anti-money laundering controls include knowing your customers, software filtering, and implementing holding periods.
What is Money Laundering?
Money laundering refers to the process of taking illegally obtained money and making it appear to have come from a legitimate source. It involves putting the money through a series of commercial transactions in order to "clean" the money.
For example, money may be placed in a business and disguised as sales revenue Sales Revenue Sales revenue is the income received by a company from its sales of goods or the provision of services. In accounting, the terms "sales" and in order to camouflage its origin. Money laundering is illegal in itself.
Money Laundering – Process
The figure below shows the three steps in money laundering and some of the controls that are used to prevent it. Money laundering is carried out through placement in a financial institution carrying out a series of transactions to disguise its original source (layering) and obtaining/using the cleaned money (integration).
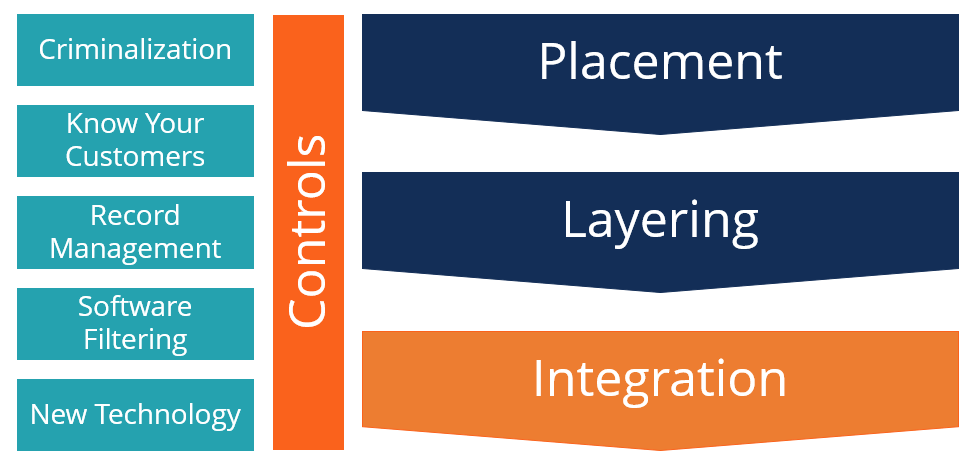
Anti-Money Laundering – Controls
1. Criminalization
Many governments, financial institutions, and businesses impose controls to prevent money laundering. The first is criminalization by the government. The United Nations Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime has set forth guidelines that help governments to prosecute individuals involved in money laundering schemes.
2. Know Your Customers
Financial institutions must also have "know your customer" policies in place to help prevent money laundering. This involves monitoring the activity of clients and understanding the types of transactions that should raise red flags. Financial institutions are required to report suspicious activity to a financial investigation unit.
3. Record Management and Software Filtering
Financial institutions and businesses also keep detailed records of transactions and implement software that can flag suspicious activity. Customer data can be classified based on varying levels of suspicion, and transactions denied if they meet certain criteria.
4. Holding Period
Many banks Retail Bank Types Broadly speaking, there are three main retail bank types. They are commercial banks, credit unions, and certain investment funds that offer retail banking services. All three work toward providing similar banking services. These include checking accounts, savings accounts, mortgages, debit cards, credit cards, and personal loans. require deposits to remain in an account for a designated number of days (usually around five). This holding period helps manage risk associated with money being moved through banks to launder money.
5. New Technology
The technology used to identify suspicious activity linked to money laundering continues to evolve and become more accurate. Technologies, such as AI and Big Data software, allow these systems to become more sophisticated.
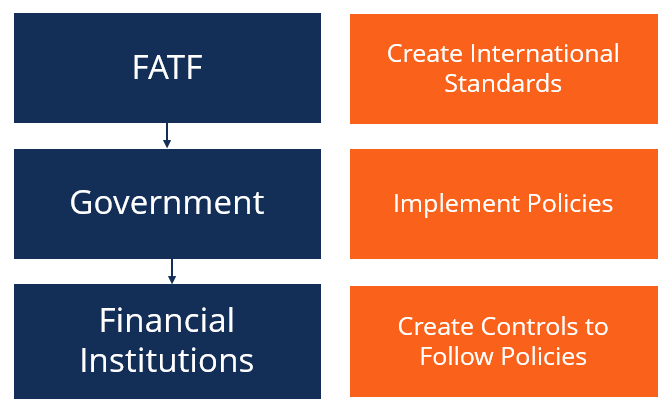
History of Anti-Money Laundering
The first anti-money laundering structures came about with the Financial Action Task Force (FATF). It ensures that international standards are put in place to prevent money laundering.
Since the 2001 terrorist attacks, the FATF now also includes terrorist surveillance in an effort to mitigate terrorist financing. Recently, cryptocurrency Cryptocurrency Cryptocurrency is a form of digital currency that is based on blockchain networking. Cryptocurrency like Bitcoin and Ethereum are becoming widely accepted. has come under scrutiny, as it provides anonymity to its users. This has facilitated a lower-risk method for criminals to go about their transactions.
Anti-Money Laundering in Financial Institutions
Financial institutions are held to high standards with regards to following procedures to identify money laundering. All bank employees are trained to some degree to identify and monitor suspicious customer activity. Larger financial institutions will also have dedicated departments to track fraud and money laundering.
Many of the institutions put in place a "know your client" measure, which can help flag suspicious transactions based on particular clients. Transactions and processes at financial institutions are recorded extensively so that law enforcement can trace the crimes back to the source.
While such institutions are legally obligated to follow anti-money laundering regulations as they relate to the country they operate in, not all agree with them. Implementing the policies are often costly and ineffective, and the net benefit of having them in place often comes into question.
Case Study: HSBC Money Laundering Scandal
HSBC went through a period of restructuring and cost-cutting, which caused them to decrease the size of their compliance department. As a result, many of the control systems to detect fraud and money laundering were weakened.
It was later found that HSBC had facilitated transactions that involved terrorist groups in the Middle East and drug cartels in Mexico. HSBC would eventually pay a fine of $1.9 billion, as regulators agreed that their control processes were inefficient in catching suspicious activity.
Related Readings
CFI offers the Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA)™ Program Page - CBCA Get CFI's CBCA™ certification and become a Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst. Enroll and advance your career with our certification programs and courses. certification program for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following resources will be helpful:
- Fraud Fraud Fraud refers to any deceptive activity engaged in by an individual with the aim of gaining something through means that violate the law. One keyword in
- Types of Due Diligence Types of Due Diligence One of the most important and lengthy processes in an M&A deal is Due Diligence. The process of due diligence is something which the buyer conducts to confirm the accuracy of the seller's claims. A potential M&A deal involves several types of due diligence.
- Financial Controls Financial Controls Financial controls are the procedures, policies, and means by which an organization monitors and controls the direction, allocation, and usage of its
- Top Accounting Scandals Top Accounting Scandals The last two decades saw some of the worst accounting scandals in history. Billions of dollars were lost as a result of these financial disasters. In this
Anti Money Laundering Analyst Job Description
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/anti-money-laundering/
Posted by: nealromble.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Anti Money Laundering Analyst Job Description"
Post a Comment